This first appeared as “EHC Corner: Petunia, the worthless tobacco” in the IR-4 Newsletter 50(1):14.
Plant Information
 Modern petunia varieties we know and love are derived from two petunia species discovered in South America during the mid-1700’s through early 1800’s. The Latin name Petunia originated from one of the native Tupi-Guarani words ‘petun’ meaning ‘worthless tobacco’. Petunia is a member of the solanceaous plant family like tobacco and has similar floral and foliar characteristics.
Modern petunia varieties we know and love are derived from two petunia species discovered in South America during the mid-1700’s through early 1800’s. The Latin name Petunia originated from one of the native Tupi-Guarani words ‘petun’ meaning ‘worthless tobacco’. Petunia is a member of the solanceaous plant family like tobacco and has similar floral and foliar characteristics.
There are 20 species of petunia, which originated in South America. The modern petunia arose from hybridization between Petunia axillaris and Petunia violaceae. In the 1800’s plant breeders searched for double flowered cultivars or fringed petals and those with other traits such as upright growth habit versus trailing. During the 1950’s the first of the modern cultivar types was developed – Grandiflora. Grandiflora’s are known for blooms measuring as large as 5” across, but they can become spindly by midsummer. Multiflora petunias have smaller flowers and more compact plants and hold up better in windy areas and rainy weather. Milliflora petunias have 1 to 1.5” blooms on very compact plants. Spreading, or Wave, petunias were developed during the 1990’s and grow 2 to 4 feet wide with blooms about 2 inches across.
Petunias thrive in full sun and are typically pollinated by lepidopterans (moths such as hummingbird hawk moth).
Economics
According to the USDA NASS Census of Horticulture 2014, petunia in the US have a wholesale value of $201M and are the third highest in terms of units (containers & flats) sold with more than 51 million produced annually.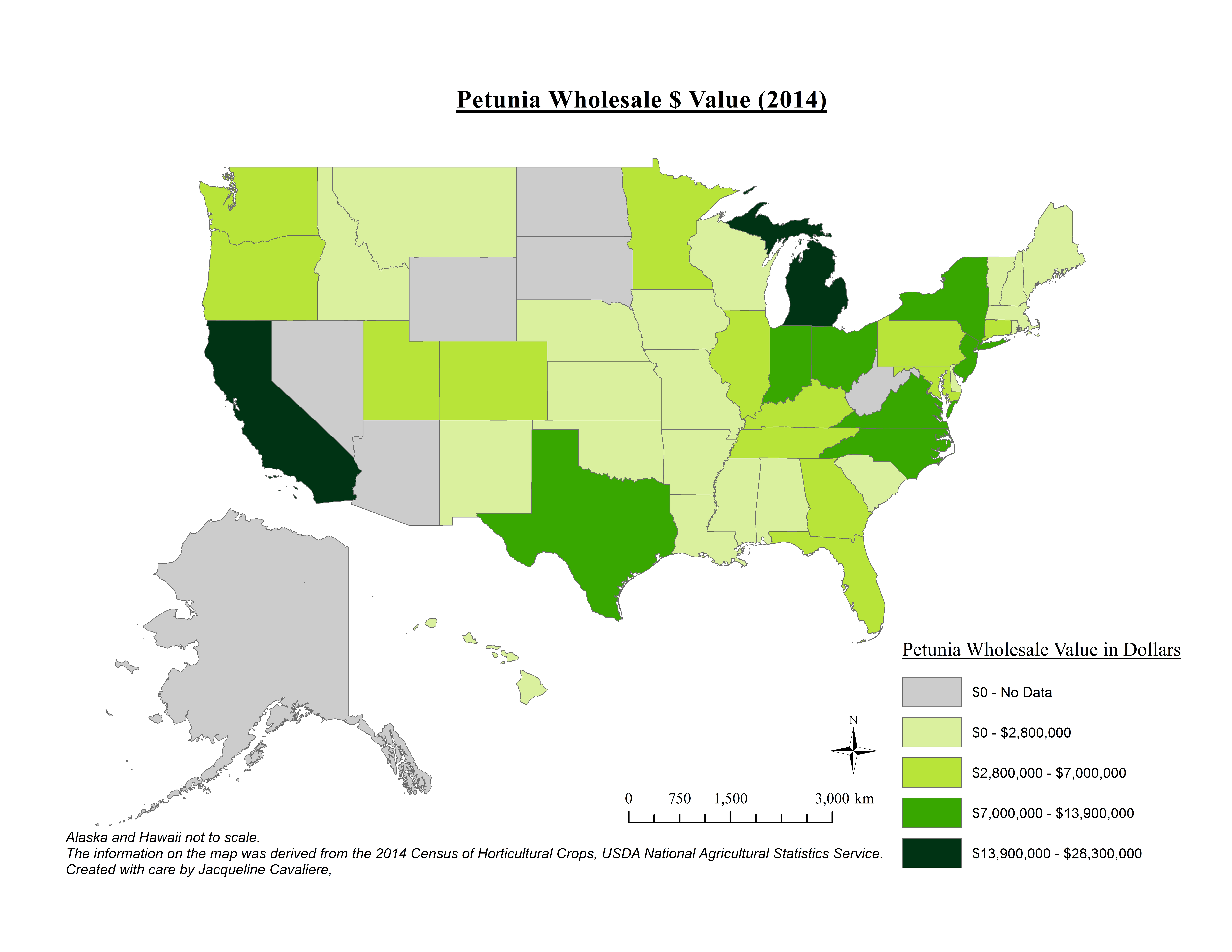
Main Disease & Pest Problems

Petunias have several main disease problems including Botrytis blight, Phytophthora crown rot, Fusarium wilt, Rhizoctonia root rot, and Impatiens nectoric spot virus.
Petunias have a wide variety of pests such as snails/slugs, tobacco hornworms, budworms, aphids, spider mites, thrips and whiteflies cause issues.
IR-4 Research
Most of the research IR-4 has sponsored has been related to crop safety (170 trials with 47 products), but we have screened new actives and products with petunia for effective management of Pythium aphanidermatum, Rhizoctonia solani and western flower thrips.
Sources Cited
https://horticultural-history.blogspot.com/2016/08/1890s-mostly-petunia-history-by-lh.html
https://www.esbenshades.com/jzv/inf/ABriefHistoryOfThePetunia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Petunia
https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/ornamental/flowers/petunia/different-petunia-flowers.htm
USDA-NASS Census of Horticulture, 2014.


