Plant Information

Coleus, also commonly known as painted nettle, flame nettle, and painted leaf, is a native of Southeast Asia through to Australia. In the most recent taxonomic classification, coleus now belongs to the genera Plectranthus and Solenostemon in the family Lamiaceae. The common garden Coleus (Coleus blumei = Plectranthus scutellarioides = Solenostemon scutellarioides) is a popular plant for its brightly colored foliage. The leaves of these plants grow in eye-catching colors including white, yellow, red, pink, purple, maroon, copper, and a wide range of greens. Coleus also have a wide variety of leaf sizes and overall shapes. Coleus breeding during the middle of last century produced an improved range of cultivars that led to it becoming the tenth most important bedding crop in the US by the 1980’s.
Coleus makes an attractive addition indoors or outdoors, although it does not tolerate cold weather and should be brought indoors once the temperature drops below 50º F. Coleus prefers bright, but indirect sunlight. If direct sunlight touches the plants leaves the colors become less brightly colored. Outside this plant needs total shade or only the most mild morning sunlight. A greenhouse environment is a good choice for Coleus blumei.
Economics
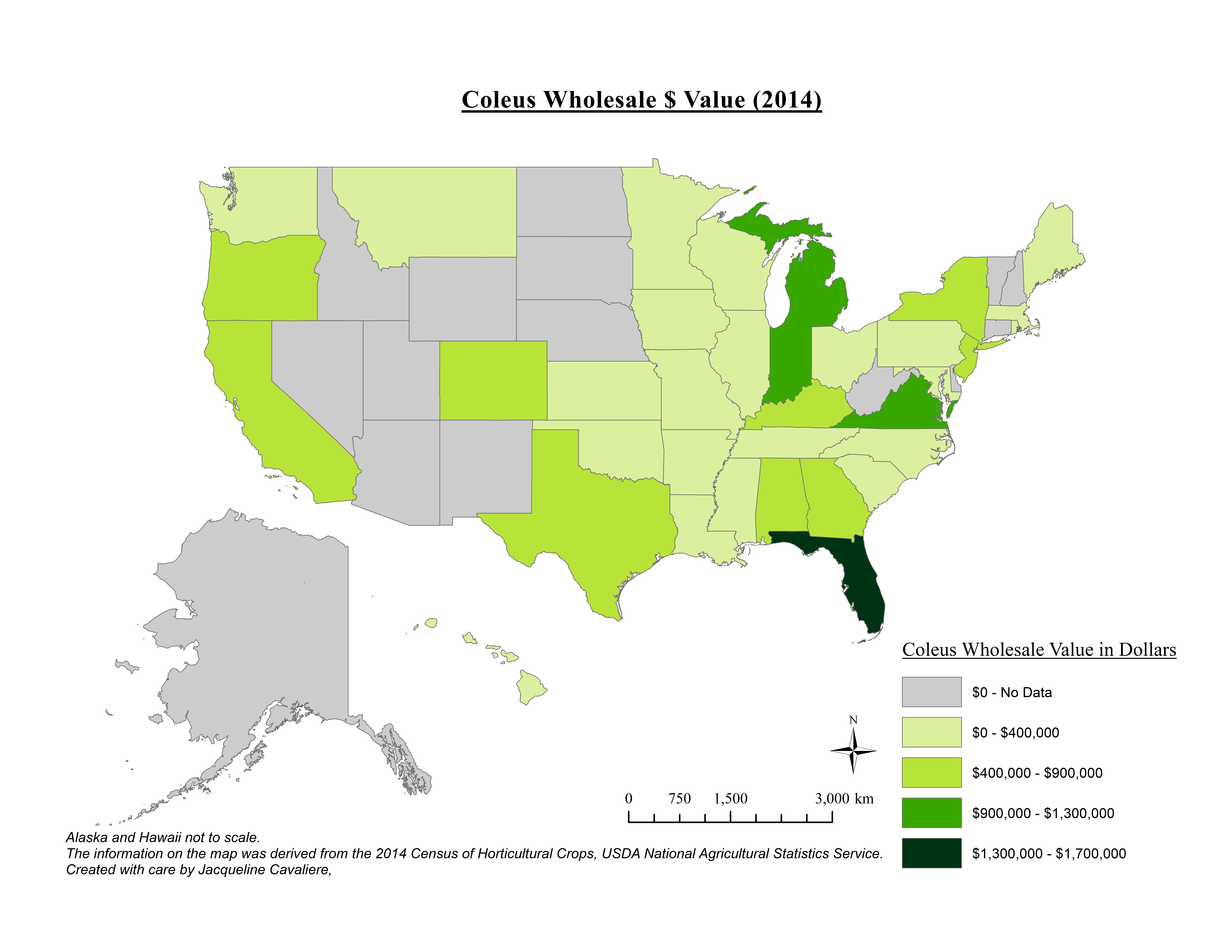
According to the USDA NASS Census of Horticulture 2014, coleus has a value of $14.3 million dollars annually. This crop is grown throughout the US with 9 states (CA, FL, GA, IL, MI, MN, NY, OR, and VA) producing the most wholesales annually.
Main Disease Problems
Two important diseases of coleus are the downy mildew (Peronospora lamii) that makes leaves brownish and can also cause leaf curling and twisting, and the impatiens necrotic spot virus which causes brown or yellow spots on leaves, rings, black or brown stem discoloration, and brown leaf veins, ultimately resulting in plant death. Foliar nematodes (Aphelencoides sp.) can also cause leaf discoloration.
Main Pest Problems
Coleus have a wide variety of pests such as thrips (which vectors impatiens necrotic spot virus), twospotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae), cyclamen mite (Phytonemus pallidus), greenhouse whiteflies (Trialeurodes vaporariorum), mealybugs ( Planococcus sp.), fungus gnats and slugs.
IR-4 Research
IR-4 has sponsored research with coleus on new actives and products for effective management of downy mildew (Peronospora sp.), and for assessment of herbicide crop safety.
Sources Cited
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plectranthus_scutellarioides
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coleus
https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/ornamental/foliage/coleus/coleus-plant-blooms.htm
https://extension.psu.edu/impatiens-necrotic-spot-virus
https://ag.umass.edu/greenhouse-floriculture/fact-sheets/downy-mildew-of-coleus
https://portal.ct.gov/CAES/Plant-Pest-Handbook/pphC/Coleus-Coleus
USDA-NASS Census of Horticulture (2014).
Authors
Ely Vea, IR-4 Environmental Horticulture Program Assistant Manager, Jackie Cavaliere, IR-4 Environmental Horticulture Program Coordinator, and Cristi Palmer, IR-4 Environmental Horticulture Program Manager


